Paper
Electric furnace steelmaking is slag smelting. You must understand slag related knowledge!
Updated: 2022-04-26 Attention:
Electric furnace steelmaking is slag smelting. You must understand slag related knowledge!
Slag is an important phase involved in various metallurgical reactions, and plays a role in removing impurities in steel and protecting molten steel. Keeping slag in good condition at all stages of EAF steelmaking is one of the important conditions for producing high-quality steel.

1、 Source of slag
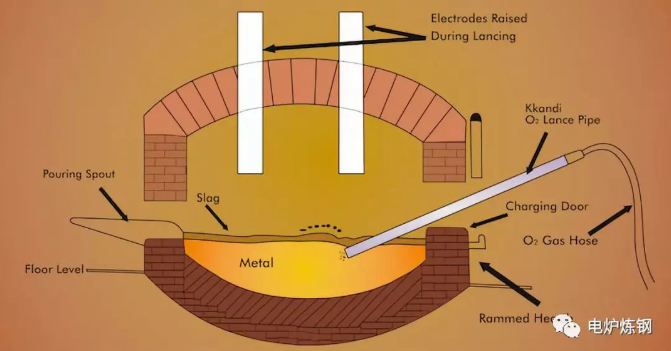
At each stage of EAF steelmaking, the surface of molten steel is covered with slag, which mainly comes from the following four aspects:
1) Slagging materials, such as lime, limestone, silica sand, fluorite, iron ore, carbon powder, ferrosilicon powder, refractory brick fragments, etc., are deliberately added for smelting purposes.
2) The products in the smelting process are mainly oxides or sulfides of various elements contained in steel, such as FeO, MnO, SiO2, Cr2O3, etc.
3) The acidic slag and alkaline SiO2 in the furnace slag are eroded into the refractory lining.
4) Impurities brought in by various raw materials.
2、 Classification and composition of slag
During steelmaking, slag is an important phase involved in various metallurgical reactions. Therefore, the slag used in different steelmaking processes and at different smelting stages is different.
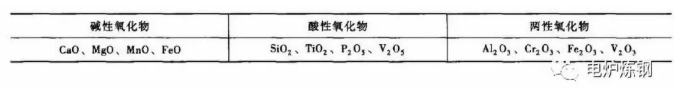
1) The lining of electric arc furnace is divided into alkaline and acidic, and the slag used is also divided into alkaline and acidic. Alkaline oxides are dominant in slag, which is called alkaline slag; Acidic oxides are dominant in slag, which is called acidic slag. See Table 1 for the classification of common oxides in slag according to acid and alkali properties.
Table 1 Classification of common oxides in slag
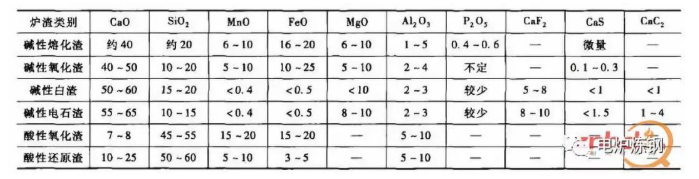
2) According to the smelting stage, the slag can be divided into melting slag, oxidation slag and reduction slag. The slag in the reduction period of alkaline electric arc furnace can be divided into white slag and carbide slag.
3) The physical and chemical properties of slag are determined by its composition. In the physical properties of steel-making slag, the most concerned is viscosity; Chemical properties are alkalinity and oxidation (or reduction) strength. Slag is mainly composed of various oxides, such as SiO2, Cao, Al2O3, MgO, FeO, MnO and P2O5. In addition, there is a small amount of sulfide, such as CAS, FES and MNS. The general composition of various slags during EAF steelmaking is shown in Table 2.
Table 2 approximate composition (mass fraction) of various slags
3、 Function of slag
In the process of steelmaking, slag has the following functions.
1) The oxidation and reduction of molten steel are controlled by slag. The main links of steelmaking process are oxidation and reduction. During the oxidation period, some elements in liquid steel should be oxidized; During the reduction period, the residual oxygen in the molten steel shall be removed. To control the oxygen content in molten steel, the FeO content in slag must be controlled.
2) Phosphorus and sulfur are harmful impurities in steel. The removal of P and s depends on slag with appropriate composition and strong binding ability with phosphorus oxide or sulfide to transfer it from liquid steel to slag.
3) The temperature of the arc column is very high, which can make the gas dissociate into ionic state and be absorbed by the liquid steel. The slag covered on the surface of the liquid steel has a good protective effect on the liquid steel and can reduce the invasion of gas. The slag has high temperature and low thermal conductivity, which can reduce the heat loss of molten steel and stabilize the temperature.
4) Protect the furnace lining. The slag layer can encircled the arc, reduce its radiation erosion to the lining, and produce better foam slag.
5) Remove non-metallic inclusions. The charge of steelmaking is often mixed with impurities such as sand, oxides generated by the oxidation of various elements, damaged and peeled furnace lining refractories, etc. if mixed into steel, they will become non-metallic inclusions. When the melting point of Al2O3 and SiO2 is high, they are easy to be separated from the molten steel slag, but many of them are in the melting point of 1710 ℃, which can not be formed when the melting point of Al2O3 and SiO2 is high.
4、 Viscosity of slag
Viscosity is an index reflecting the viscous resistance of liquid flow. When the liquid moves in laminar flow, there is friction resistance between the liquid layers, which hinders the liquid flow. This internal friction resistance is one of the characteristics of the liquid. The viscosity of liquid is the opposite concept of fluidity. The higher the viscosity, the worse the fluidity. There are generally three kinds of viscosity, namely dynamic viscosity, kinematic viscosity and conditional viscosity. It is usually referred to as "viscosity". Unless otherwise specified, it refers to dynamic viscosity.
The friction resistance generated by the relative motion of each liquid layer is directly proportional to the contact area between the layers and the relative motion speed between the layers. The proportional constant between them is the dynamic viscosity of the liquid, which is commonly used as the symbol η, The unit is Pascal seconds (Pa.s). The kinematic viscosity of a liquid is obtained by dividing its dynamic viscosity by its density. Conditional viscosity is the viscosity measured by various calibrated viscometers, such as Engler viscosity, flow cup viscosity, etc.
Viscosity is one of the important physical properties of slag. It has a great influence on the reactions between liquid steel and slag, the escape of gas in steel, the transfer of heat and even the service life of furnace lining. The efficiency of dephosphorization and desulfurization and the speed of oxidation and reduction reaction all depend on the diffusion speed of reactants in the slag.
The slag viscosity is too high, which is unfavorable to many metallurgical reactions between liquid steel and slag. For example, during decarbonization in oxidation period, the resistance of CO bubbles discharged through slag is very large, which will slow down the progress of carbon oxygen reaction; During reduction, the reaction of diffusion deoxidation will also be greatly affected. The same is true of dephosphorization and desulfurization.
Too low viscosity is also harmful. If the slag is very thin, it is not easy to absorb the heat of the arc column, and the part reflected to the furnace cover and furnace wall increases, which is not conducive to the control of liquid steel temperature, but also shorten the service life of the furnace lining. At the same time, the slag with low viscosity and good fluidity also has a strong direct erosion and flushing effect on the furnace lining.
In actual production, it is very important to keep the viscosity of slag stable.
In the alkaline furnace, the addition of acid oxide can reduce the viscosity, while the addition of alkaline oxide will increase the viscosity. The situation of acid slag is the opposite. However, there are exceptions. Although FeO is an alkaline oxide, it can reduce the viscosity of alkaline slag because of the low melting point of FeO itself.

5、 Conductivity of slag
Slag has conductivity because charged ions and free electrons can flow under a certain voltage, which plays a very important role in EAF steelmaking. There are two main factors affecting the conductivity of slag.
1) The higher the content of alkaline oxide in slag, the stronger the conductivity; The higher the fluorescence content of acid oxides, the weaker the conductivity. Therefore, the conductivity of acid slag is not as good as that of alkaline slag.
In addition, low-cost oxides (such as FeO) in slag will enhance its conductivity, so the conductivity of oxidized slag is better than that of reduced slag. Cao can also improve the conductivity of slag. In acidic slag, Cao can reduce the viscosity of slag and affect the conductivity more obviously.
2) As the temperature of slag increases, the activation energy of charged ions and free electrons increases, and the conductivity increases with the increase of temperature.
Source: electric furnace steelmaking


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp